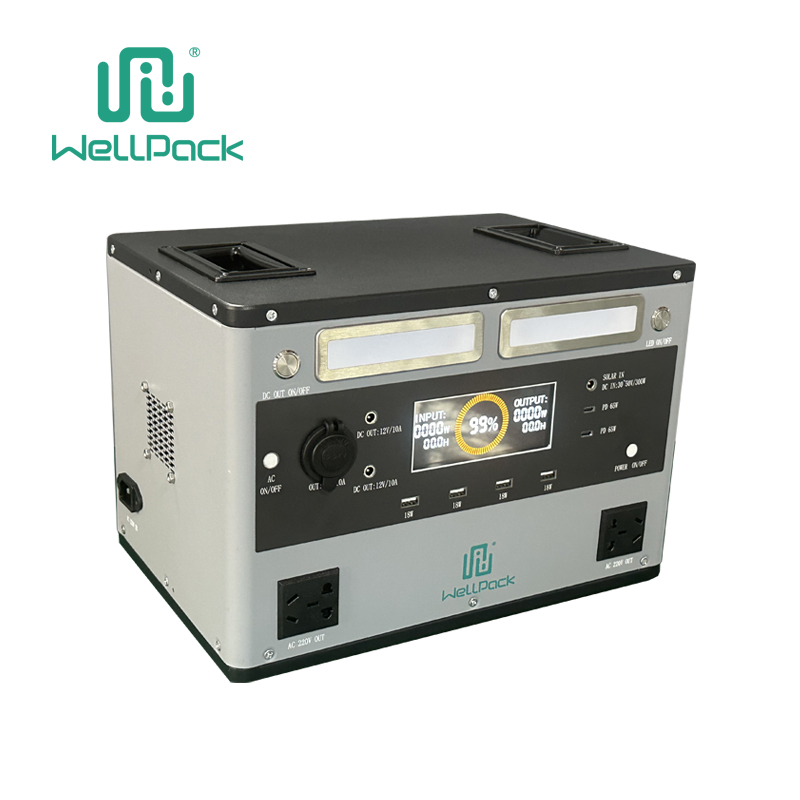
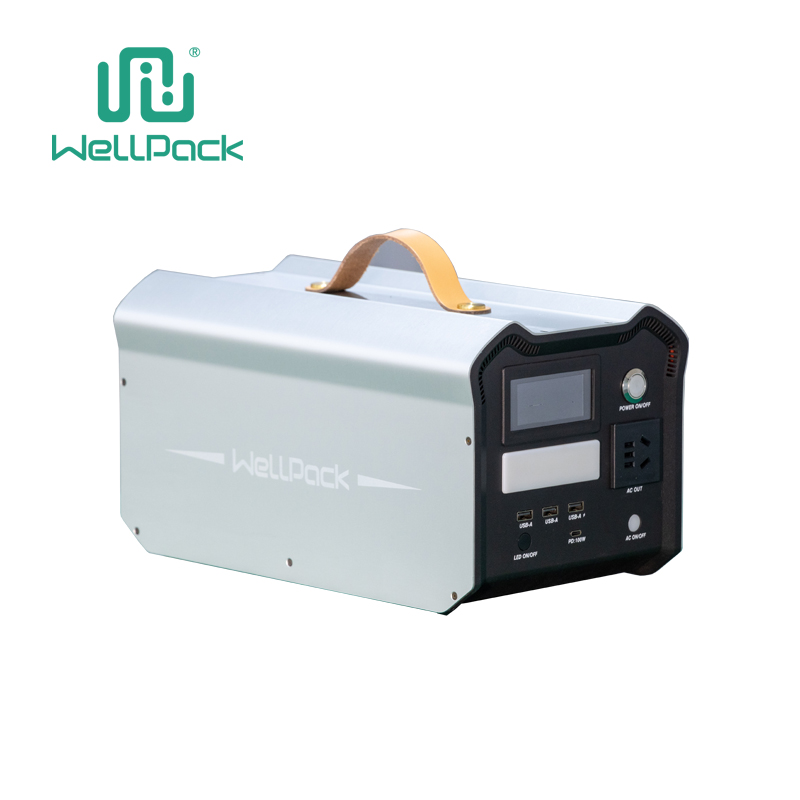
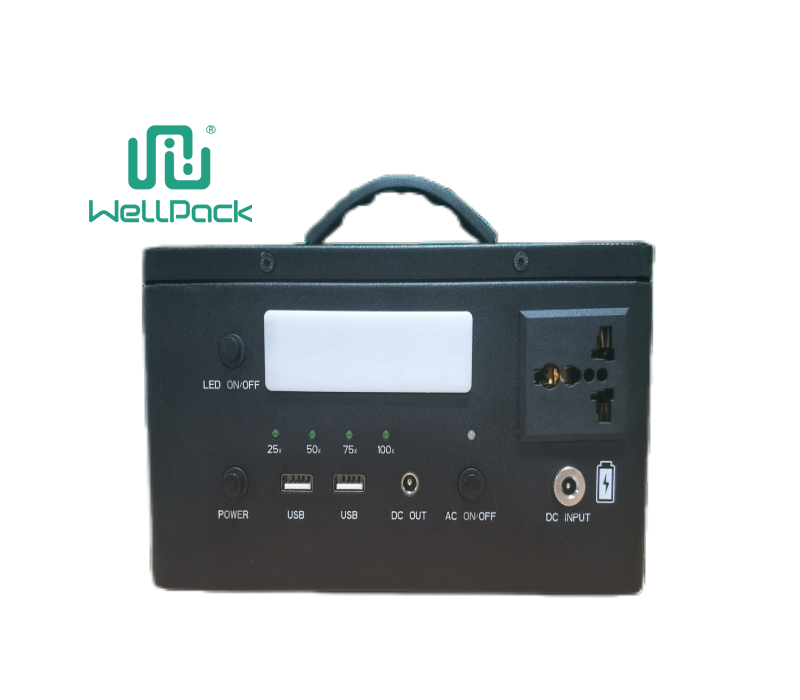
If you have ever used a device that runs on battery power, such as a laptop, a smartphone, or a flashlight, you have probably encountered an inverter. An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. DC electricity is the type of electricity that flows in one direction, like in a battery. AC electricity is the type of electricity that changes direction periodically, like in a wall socket.
Why do we need inverters?
Well, most of the appliances and devices that we use in our homes and offices run on AC electricity, because it is more efficient and safer to transmit over long distances. However, some of the sources of electricity that we use are DC, such as solar panels, wind turbines, or batteries. Therefore, we need inverters to convert DC electricity into AC electricity so that we can use it for our appliances and devices.
How do inverters work?
There are different types of inverters, but the basic principle is the same. An inverter consists of two main components: a switch and a transformer. The switch is used to change the direction of the DC current periodically, creating a pulsating DC current. The transformer is used to increase or decrease the voltage of the pulsating DC current, depending on the output voltage required.
The switch can be either mechanical or electronic. A mechanical switch is a physical device that opens and closes the circuit at regular intervals. An electronic switch is a device that uses transistors or other components to control the flow of current electronically. Electronic switches are more common and efficient than mechanical switches.
The transformer can be either step-up or step-down. A step-up transformer increases the voltage of the pulsating DC current, while a step-down transformer decreases it. The output voltage of the inverter depends on the ratio of the number of turns in the primary and secondary coils of the transformer.
The output waveform of the inverter can be either pure sine wave, modified sine wave, or square wave. A pure sine wave is a smooth and continuous waveform that resembles the AC electricity from the grid. A modified sine wave is a stepped waveform that approximates a pure sine wave. A square wave is a simple on-off waveform that has sharp edges and corners. The output waveform affects the quality and efficiency of the AC electricity delivered by the inverter.
The type of inverter you need depends on your application and budget. Pure sine wave inverters are more expensive but provide better quality and compatibility with sensitive devices. Modified sine wave inverters are cheaper but may cause some interference or damage to some devices. Square wave inverters are the cheapest but are only suitable for simple devices that do not require precise voltage or frequency.
Inverters are useful and versatile devices that enable us to use different sources of electricity for our needs. By understanding how they work, you can choose the best inverter for your situation and enjoy its benefits.